Managing Gastroparesis Diet for Better Digestion in 2025
Gastroparesis, a condition affecting the stomach’s ability to empty its contents, can lead to nausea, vomiting, and a range of digestive challenges. Managing a gastroparesis diet is essential for promoting better digestion, reducing symptoms, and improving overall health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll discuss effective strategies for creating an optimal diet plan for gastroparesis, revealing the best foods to include, cooking methods to adopt, and dining practices to follow.
Understanding Gastroparesis and Its Impact on Nutrition
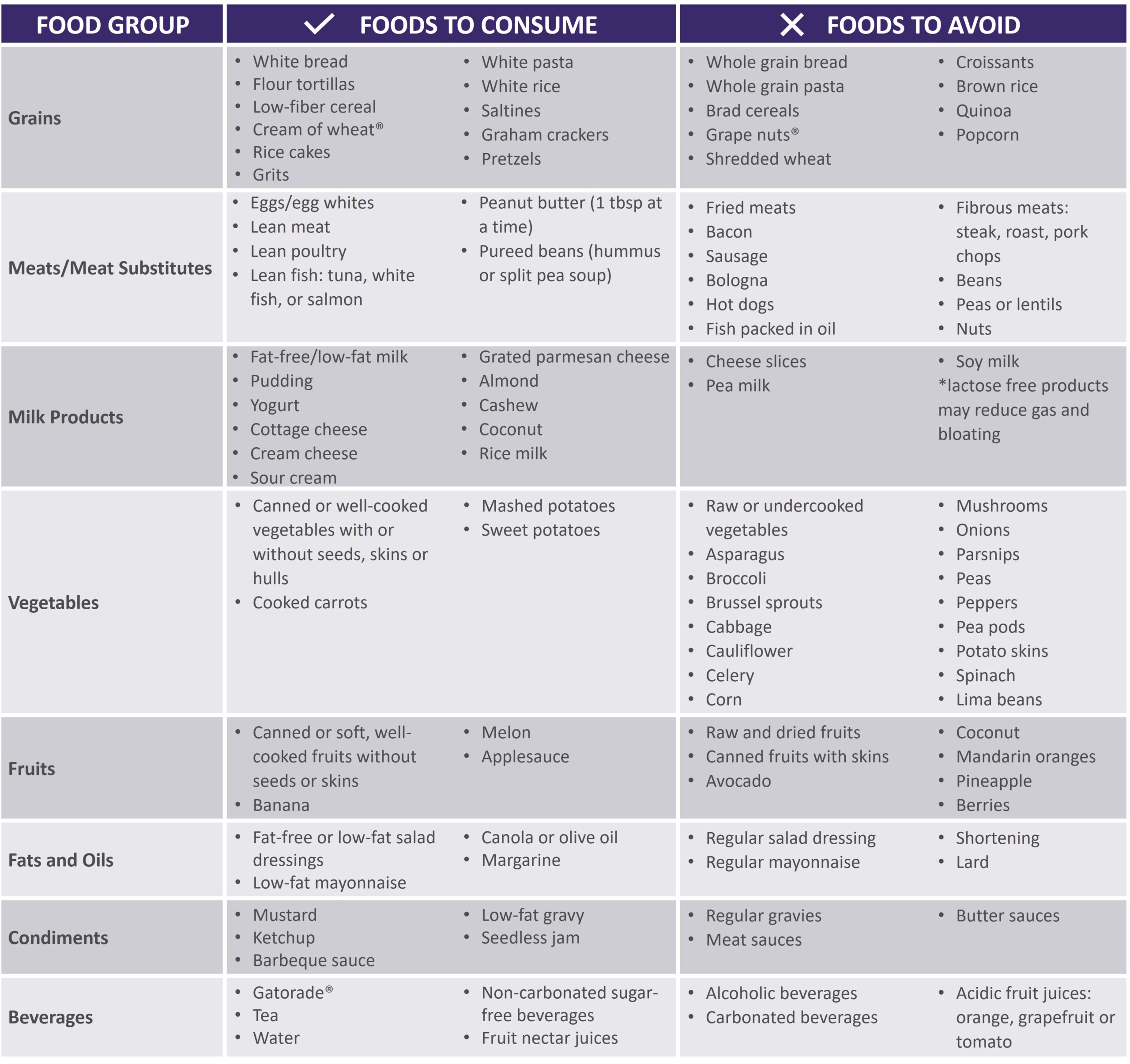
A key aspect of managing gastroparesis involves understanding the condition and its dietary implications. Gastroparesis can significantly alter digestive health by slowing the passage of food through the stomach. Identifying appropriate foods for gastroparesis becomes crucial for symptom relief. Individuals are advised to focus on low-fiber foods and easily digestible meals that reduce the burden on the gastrointestinal system.
Recognizing Gastroparesis Symptoms
Common gastroparesis symptoms include abdominal pain, a feeling of fullness after eating just a small amount, and bloating. These symptoms can often make meal planning more challenging. It’s essential to monitor how different foods affect personal comfort levels. Keeping a food diary can aid in identifying specific food triggers that may exacerbate symptoms. For example, foods high in fat can slow down digestion, making them less suitable.
Impact of Low-Fiber and Soft Diets
Adopting a low-fiber diet rich in soft foods can alleviate discomfort for those with gastroparesis. Foods such as mashed potatoes, applesauce, and well-cooked vegetables that are easy to chew and swallow contribute to more efficient digestion. Additionally, individuals should avoid foods with high fiber content, such as raw fruits and whole grains, as they can lead to bloating and discomfort.
Consulting Healthcare Professionals
For personalized dietary adjustments, working with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian, is critical. A dietitian can provide individualized nutrition advice based on personal symptoms and lifestyle. This professional guidance ensures that individuals with gastroparesis can maintain a nutritious and balanced diet while managing their condition effectively.
Building a Balanced Gastroparesis Diet
Creating a balanced gastroparesis diet involves careful planning and analysis of food intake. The incorporation of specific protein sources, healthy fats, and calorie-dense options is essential to prevent malnutrition and weight loss that may occur due to poor nutrient absorption. Here are some vital components to consider.
Choosing Suitable Protein Sources
Protein is crucial for health, requiring special consideration in a diet for gastroparesis. Options such as eggs, fish, and tender meats contribute to the necessary intake without overloading the digestive system. Incorporating gastronomic techniques, such as using gentle cooking methods like steaming or slow cooking, allows proteins to become easier to digest.
Incorporating Calorie-Dense Options
Maintaining energy levels and nutritional balance can be achieved through high-calorie foods. Foods like nut butters, avocado, and full-fat dairy products can provide energy without significant bulk. Additionally, opting for liquid diets might benefit individuals struggling with solid food consumption, making smoothies with nutrient-rich ingredients an excellent alternative.
Meal Frequency and Portion Control
Implementing meal frequency strategies is vital in managing gastroparesis effectively. Smaller meals consumed more frequently can minimize bloating and discomfort. Portion control is equally important; individuals are encouraged to use measuring cups to help restrict meal sizes and adhere to a dietary guideline that facilitates easier digestion while providing essential nutrients.
Effective Cooking Techniques and Meal Prep Strategies
Utilizing effective cooking techniques makes a significant difference in your gastroparesis foods. Opting for cooking methods that maintain the nutrition of the food while enhancing digestibility is crucial for symptom management. Preparing easy-to-digest meals using gentle cooking methods, like blanching or baking, can significantly improve digestion and nutrient availability.
Soft Diet Recipes and Preparation
Soft diet recipes tailored to those managing gastroparesis often include pureed soups, stewed fruits, and scrambled eggs. A practical meal prep idea is to prepare these dishes in batches and store them in portioned containers for convenience. This approach ensures easy access to nutritious meals at any time while also adhering to prescribed dietary restrictions.
On-the-Go Meal Planning
Easily accessible, nutritious snacks for individuals living with gastroparesis can significantly enhance quality of life. Keeping snacks like yogurt, cottage cheese, or pre-cut soft fruits ready allows for quick meals on busy days. Including meal replacement drinks can also provide additional calorie intake while being easier to consume than solid foods.
Hydration and Managing Symptoms
Hydration plays a crucial role in maintaining digestive health. A focus on drinking sufficient fluids, particularly electrolyte balance, is essential for individuals with gastroparesis. Staying well-hydrated can support digestion by preventing constipation and promoting overall well-being.
Hydration Tips and Strategies
Including suitable beverages such as herbal teas and non-carbonated drinks in a hydration strategy can promote better hydration without causing discomfort. Moreover, considering electrolyte-rich options during times of sickness or excessive sweating helps maintain proper body functions. Sparkling water may exacerbate symptoms for some, so monitoring personal triggers is essential.
Managing Nausea and Other Challenges
Individuals managing chronic nausea as a symptom of gastroparesis should focus on environmental adjustments and dietary tweaks. Incorporating calming techniques and avoiding strong odors may yield short-term relief. Yet, keeping a food diary to document food intake can greatly aid in determining which foods to limit and which foods remain digestible.
Key Takeaways
- Prioritize a low-fiber, soft diet to enhance digestion and alleviate symptoms.
- Consult healthcare professionals for personalized dietary advice.
- Incorporate high-calorie, nutrient-dense options to maintain energy levels.
- Use gentle cooking methods for better nutrient absorption.
- Focus on hydration and managing symptoms effectively through dietary strategies.
FAQ
1. What are the recommended foods for a gastroparesis diet?
Recommended foods for a gastroparesis diet include soft, low-fiber options such as well-cooked vegetables, avocados, eggs, and protein smoothies. Avoiding high-fiber and high-fat foods can improve digestion, making meal choices crucial for managing symptoms.
2. How can I track food triggers related to gastroparesis?
Keeping a food diary can be an effective strategy to identify food triggers. Documenting the foods consumed, symptoms experienced afterward, and portion sizes can provide insights into foods to avoid or include in your diet.
3. Are there specific cooking techniques that benefit gastroparesis?
Gentle cooking methods, including steaming, slow cooking, or pureeing food, can make meals easier to digest, thus improving gastrointestinal comfort. Preparing dishes like smooth soups or mashed vegetables can be particularly effective.
4. How important is hydration for managing gastroparesis?
Hydration is essential for individuals with gastroparesis, as adequate fluid intake can prevent constipation and support nutrient digestion. Staying well-hydrated through electrolyte-rich beverages can mitigate some symptoms linked to dehydration.
5. Can stress impact my gastroparesis symptoms?
Yes, managing stress is crucial as it may exacerbate gastroparesis symptoms. Engaging in relaxation techniques or mindfulness could aid in reducing symptom severity and improve overall digestive health.
6. Is it necessary to consult a dietitian for gastroparesis management?
Consulting a dietitian is highly recommended for personalized nutrition advice. A professional can offer tailored dietary strategies and help create a nutritional therapy plan that accommodates individual needs and preferences.
7. What common mistakes should I avoid with a gastroparesis diet?
Common mistakes include consuming high-fat or high-fiber foods, skipping meals, and neglecting to monitor portion sizes. It’s also essential to stay aware of fluid intake to prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate symptoms.