Effective Diet Chart for 1 to 3 Month Pregnancy: Discover Healthy Meal Options for Expecting Mothers in 2025!
Understanding the Basics of Pregnancy Diet
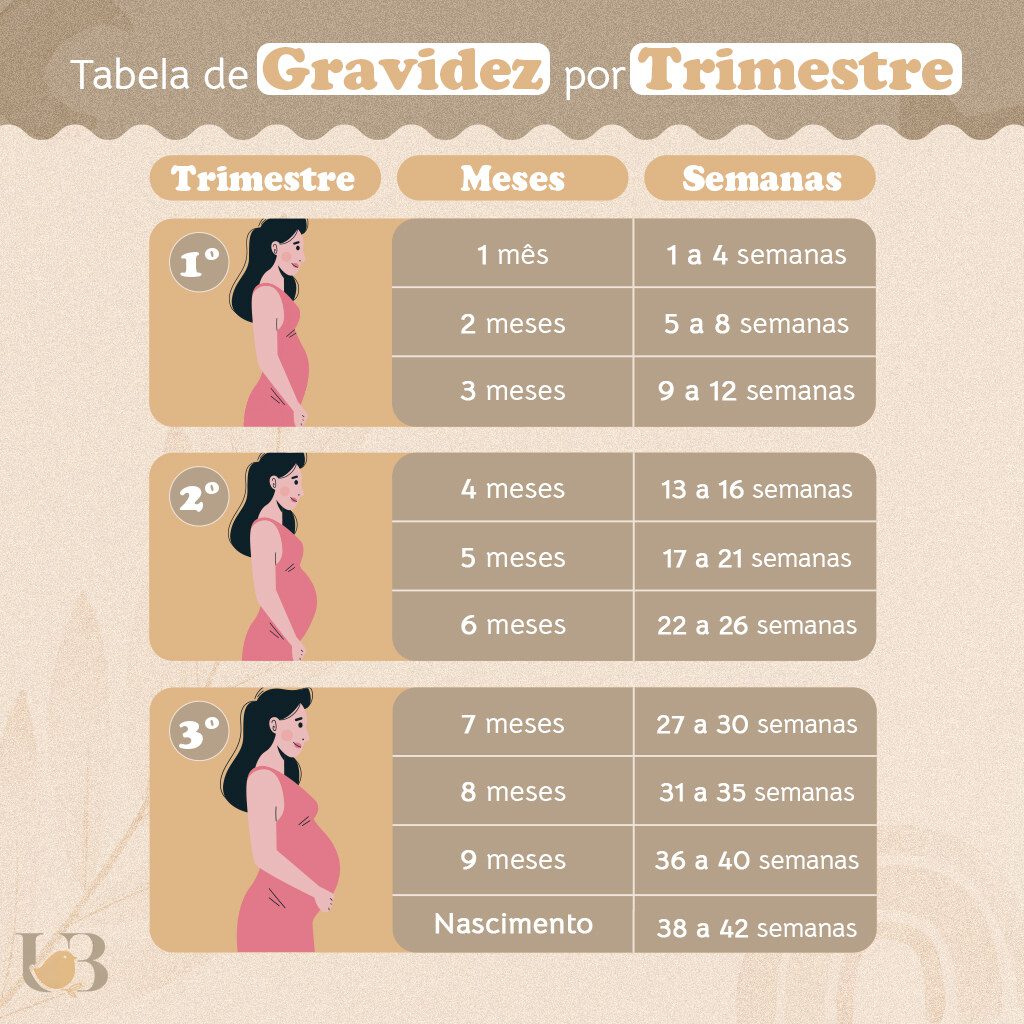
During the first trimester, a well-structured pregnancy diet is crucial for both the mother and the developing baby. It’s essential to focus on balanced nutrition that incorporates a variety of food groups. Emphasizing essential nutrients such as folic acid, iron, and Omega-3 fatty acids is fundamental for fetal growth and development. Pregnant women should consider including a mix of fruits for pregnancy, vegetables for pregnancy, protein sources, whole grains, and dairy products in their daily meals. Moreover, it is advisable to manage cravings while maintaining proper portion control and hydration. A confident approach to planning meals can significantly enhance wellness during this early stage.
The Role of Prenatal Vitamins
Consulting with a healthcare professional to determine appropriate prenatal vitamins is vital for expectant mothers. These vitamins supplement the diet, providing essential micronutrients that may not be sufficiently obtained through food alone. For instance, folic acid sources like leafy greens and legumes support neural tube development, whereas iron-rich foods, such as spinach and red meat, help prevent anemia. Incorporating a good quality nutritional supplement can also provide key micronutrients. In addition, awareness about the timing of meals and snacks can enhance the absorption of these nutrients.
Navigating Dietary Limits: Foods to Avoid
It’s important for pregnant women to understand what foods to avoid during this critical period. Certain foods can pose risks like food poisoning or harm the developing fetus. For example, raw fish or undercooked meats can introduce harmful bacteria. Expecting mothers should stay away from unpasteurized dairy products, certain seafood high in mercury, and processed foods laden with preservatives. Ensuring food safety during pregnancy and being mindful of hydration suggestions can contribute to a safer, healthier pregnancy diet.
Structuring Your Pregnancy Meal Plan
Creating a comprehensive pregnancy meal plan helps in monitoring daily intake and ensuring a balanced diet. The focus should be on achieving energy needs through diverse meals rich in nutrients. Incorporate high fiber foods, wholesome breakfasts, satisfying lunches, and nutritious dinners. Rotating between various foods that relieve nausea can support ongoing digestive health. Here are some suggested meal structures for better energy and variability.
Sample Meals for a Week
Consider structuring your week with specific meal themes. For instance, Mondays can be dedicated to enjoying vegetables to eat heavily, like steamed broccoli or carrots, paired with quinoa. Tuesdays can emphasize protein-rich meals; grilled chicken or tofu serve as excellent sources. Whole-grain toast complemented with avocado can be a healthy breakfast option on Wednesday. Shifting to seafood on Thursday introduces omega-3 fatty acids beneficial for brain development while avoiding high mercury content choices. Regularly rotating seasonal fruits and experimenting with healthy recipes promotes excitement in meals, making healthy eating enjoyable.
Cooking Methods and Meal Prep Tips
Adopting safe cooking practices is essential for maintaining nutrient value. Steaming, grilling, or baking food can help retain vitamins compared to frying. Moreover, planning ahead with meal prep for pregnancy allows mothers to save time and minimize stress. Preparing meals in advance, such as batch cooking wholesome lunches or dinners, reduces the burden on busy days. Simple strategies, like creating grocery lists beforehand and organizing kitchen essentials, set the stage for better nutritional choices.
Hydration and Managing Nausea
Staying sufficiently hydrated is one of the cornerstones of a healthy pregnancy diet. Adequate hydration tips suggest aiming for 8-10 glasses of water daily, with extra fluids required in cases of increased energy output. Packed with nutrients, smoothies made with spinach, bananas, and Greek yogurt are refreshing options while managing morning sickness. Watching sodium intake in the diet can also mitigate bloating and excess discomfort during pregnancy. Creative snacks for energy, such as oatmeal cookies with dried fruits, are both hydrating and nutritious.
Dealing with Cravings: Practical Tips
Coping with pregnancy cravings without compromising nutritional balance is crucial. Engaging in mindful eating methods helps in making informed choices. When a craving for a food to avoid arises, consider substituting with healthier alternatives. For instance, if the urge is for chips, fresh salsa with whole grain crackers can satisfy that desire while remaining within healthy parameters. Understanding your cravings through journaling your emotional state may unearth patterns and help mitigate unhealthy eating behaviors.
Individual Nutritional Needs and Lifestyle Adjustments
Expecting mothers must adapt their diets according to unique nutritional needs, which may vary based on individual health conditions. Consulting with a nutrition specialist can help personalize meal plans that address specific deficiencies, such as iron deficiency anemia. Highlighting low-carb diets or vegetarian pregnancy diets may come into play based on personal preferences. Leveraging cultural heritage through traditional pregnancy meals can also honor family legacies while ensuring the mother and child receive adequate nourishment.
Key Takeaways on Healthy Eating During Pregnancy
Adopting wholesome eating habits during the initial months of pregnancy not only ensures maternal and fetal health but also facilitates better energy management. Focus on incorporating essential nutrients, making meal plans dynamic, and paying attention to hydration and cravings. Remember, the ultimate goal is to maintain a balanced but enjoyable diet that supports all aspects of your pregnancy journey.
FAQ
1. What are the top essential nutrients needed during the first trimester?
In the first trimester, pivotal nutrients include folic acid for neural development, iron to prevent anemia, calcium for bone health, and Omega-3 fatty acids for brain function. Incorporating foods rich in these nutrients, alongside prenatal supplements, ensures both mother and baby’s health.
2. How can I manage morning sickness effectively?
To alleviate morning sickness, consider eating smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. Incorporating snacks for morning sickness, like crackers or banana bread, can also be beneficial. Additionally, staying hydrated and consuming ginger or peppermint can further mitigate symptoms.
3. Can I follow a vegetarian pregnancy diet?
Yes, a well-planned vegetarian pregnancy diet can meet all dietary needs. Focus on including a variety of proteins such as legumes and nuts, alongside iron-rich foods and dairy for calcium. Seek guidance to ensure all essential nutrients are covered without deficiencies.
4. How much weight gain is considered normal during pregnancy?
Weight gain during pregnancy varies based on individual health and nutritional needs. On average, a gain of 1-4 pounds in the first trimester and about 1 pound per week in the second and third trimesters is common. Always consult with a healthcare provider to tailor a plan according to personal situations.
5. What are safe foods for pregnancy?
Safe foods for pregnancy primarily include pasteurized dairy, well-cooked meats, fresh fruits, and vegetables. Wisely avoiding unpasteurized products, raw fish, and deli meats is crucial to prevent health issues related to food poisoning.