Smart Ways to Optimize Coyote Diet for Effective Wildlife Management in 2025
Understanding the coyote diet is vital for successful wildlife management strategies. As adaptable omnivores, coyotes play a significant ecological role, and their dietary preferences directly influence their interactions within their habitats. By optimizing the coyote food sources, wildlife managers can ensure healthier ecosystems while maintaining coyote populations that cohabit with local wildlife effectively. This article explores the complexities of what do coyotes eat, their feeding behaviors, and strategies to adaptively manage their diet while considering ecological impacts.
Understanding Coyote Feeding Habits
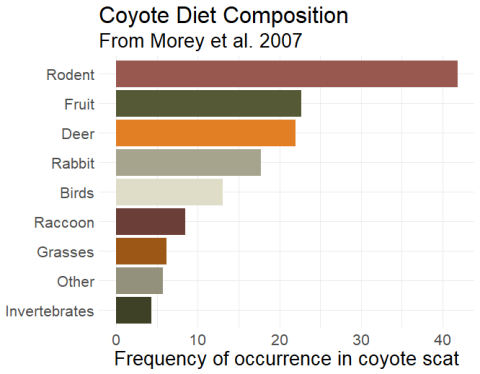
Coyote feeding habits include a diverse range of food items, which can vary based on environment and season. In urban settings, their urban coyote diet tends to lean towards human-associated foods, whereas rural areas may see more small mammals and fruits. A detailed analysis of coyote nutrition shows that they require a mixture of protein and plant matter to thrive. Understanding these habits can lead to effective wildlife management practices that leverage these choices.
Coyote Omnivore Behavior
The flexibility in the coyote diet marks them as one of the most successful omnivores in North America. Studies show that they adapt their dietary preferences based on the availability of food sources. For instance, during warmer months, coyotes exhibit increased fruit consumption, while winter typically sees a return to hunting small mammals. This adaptability highlights both their resilience and their ecological role, maintaining balance within their ecosystems.
Regional Dietary Variations
Coyotes exhibit significant diet variation based on their geographical location. For urban coyotes, human encroachment has altered their feeding patterns, including scavenging behaviors that tap into accessible waste, a factor less prevalent in rural areas. Conducted analyses indicate that rural coyote food sources are more reliant on local wildlife, including rodents and birds, demonstrating how environmental factors dictate their feeding strategies.
The Importance of Coyote Foraging
Foraging behaviors in coyotes reflect their roles as both predators and scavengers. They are known to explore vast areas—often becoming adept at coyote foraging techniques to maximize their energy efficiency. The coyote ecological role encompasses keeping prey populations in check and promoting biodiversity through their omnivorous consumption patterns. Wildlife management should, therefore, harness these foraging traits to monitor and adjust their food resources strategically.
The Impact of Coyote Nutrition on Ecosystem Balance
Coyotes’ dietary habits have profound implications for their ecosystems, informing population control measures and species conservation efforts. Given their apex predator status, they directly affect small mammal populations and, consequently, vegetation health. Optimizing their coyote prey relationships is essential for researchers and conservationists, providing insights into managing local wildlife effectively without jeopardizing coyote health.
Coyote Scavenging and Decomposer Role
Coyotes often serve a crucial role in their ecosystems as scavengers. Their tendency for coyote scavenging helps reduce carcass buildup, thus performing a decomposers role. This behavior aids in nutrient cycling within terrestrial ecosystems. Implementing managed coyote populations can lead to healthier communities for other species, showcasing their critical function in maintaining ecological balance.
Understanding Coyote Dietary Preferences
Research into coyote dietary preferences reveals that these animals can significantly regulate prey availability in their habitats. Observations show that they hunt smaller mammals extensively, contributing to coyote interactions with prey dynamics. Understanding these interactions not only aids in clearer ecological modeling but assists in predicting the potential impacts on local food webs.
Seasonal Dietary Adaptations
Coyotes are known for their capacity to adapt their dietary habits over seasons. With fluctuating food availability due to seasonal changes, wildlife managers must be aware of these seasonal food availability shifts, as they can help optimize feeding patterns, thus ensuring coyote populations remain healthy and aligned with their ecosystems. For instance, during harsher winters, coyotes may shift their focus on hunting rather than scavenging due to the scarcity of food.
Coyote Hunting Skills: Techniques and Strategies
Understanding coyote hunting strategies is pivotal for managing their populations effectively. These mammals have evolved various coyote hunting techniques tailored to their prey’s behaviors and habitat. Knowledge about these hunting patterns assists in elaborating on effective management plans, ultimately contributing to conservation practices and minimizing human-wildlife conflicts.
Coyote Interactions with Prey
Understanding how coyotes interact with their prey is crucial for comprehending their feeding strategies. They typically utilize ambush tactics and pack hunting in more effective prey capture scenarios. This recognition can lead to improved wildlife management techniques that ensure both coyote populations and their prey species remain in balance.
Coyote Adaptation to Habitat
Coyotes are highly adaptable, adjusting their diet in different habitats due to resource variability. Whether thriving in urban environments or more traditional grasslands, coyotes fine-tune their food sources to exploit available opportunities. By understanding these adaptations, wildlife managers can make informed decisions to maintain ecosystem stability.
Practical Examples of Coyote Management
Several wildlife agencies have implemented coyote population management systems that focus on dietary optimization. For instance, control measures to reduce rodent populations via targeted coyote feeding strategies have been successful in various regions. These models should be continuously assessed for effectiveness, aiming to create a sustainable coexistence between wildlife and human communities.
Key Takeaways
- Coyotes are adaptive omnivores, requiring diverse and balanced diets for health and ecological roles.
- Regional variations in diet manifest in different feeding strategies, heavily influenced by local food availability.
- Understanding peak seasonal dietary patterns helps in effective wildlife management and conservation efforts.
- Responsible management can contribute to biodiversity and ecosystem health by leveraging coyotes’ natural behaviors.
FAQ
1. What are the primary food sources for coyotes in urban areas?
Urban coyotes often scavenge human-related food items, such as garbage and pet foods, in addition to hunting small mammals like rabbits and rodents. Their diet is significantly different from that of their rural counterparts due to food accessibility and behavior modifications linked to human presence.
2. How do coyote dietary preferences change with the seasons?
Coyote dietary preferences vary seasonally, with an increased focus on small mammals and fruits during warmer months and reliance on hunting more during harsh winters. This adaptability helps them to survive in diverse habitats and changing environmental conditions effectively.
3. What role do coyotes play in animal scavenging?
Coyotes serve as crucial scavengers within their ecosystems by consuming dead plant and animal material, helping to maintain ecological balances. Their scavenging activity redistributes nutrients back into the ecosystem, supporting overall health and functioning.
4. How can wildlife management practices optimize coyote diet?
By understanding coyote food choices and seasonal variations, wildlife managers can implement habitat management strategies that encourage natural foraging behaviors and optimize food resource availability, fostering a healthier coyote population and ecosystem.
5. What impact does coyote population control have on local ecosystems?
Regulating coyote populations can directly influence prey dynamics, promoting balanced small mammal populations and supporting plant health. Responsible management practices can promote biodiversity, alleviate human-wildlife conflicts, and sustain ecological balance.
6. How have coyotes adapted their diets in response to urbanization?
Coyotes have adapted remarkably well to urban environments, incorporating more human-derived food sources, such as trash and pets, into their diet. This adaptability demonstrates their resilience and can offer insights into managing coyote populations in crowded areas.
7. Why is studying coyote dietary habits important for conservation efforts?
Understanding coyote diet studies provides valuable insight into how these animals impact their ecosystems, facilitating better management practices that ensure both coyote success and the health of the surrounding wildlife communities.